If you want to learn ethical hacking in India, this guide lays out a clear, step by step path from basics to your first job in cyber security. It focuses on practical skills, certifications, labs, and the job search process for freshers.
Why learn ethical hacking in India now?
Yes, learning ethical hacking in India is a practical route to high demand tech jobs and career growth. Cyber security skills are in short supply across enterprises, startups, and government, making this an attractive entry path for students and fresh graduates.
In this guide you will find a structured roadmap, recommended tools, certifications that employers value, and advice on building a hiring-ready portfolio. The focus is on skills you can practice, verify, and show during interviews.
What foundational skills do you need first?
The first skills to learn are basic networking, Linux, and scripting. These form the backbone of any ethical hacking or cyber security role and let you follow tools and methodologies used by professionals.
- Networking basics: TCP/IP, DNS, HTTP, ports, and common protocols.
- Linux commands and file permissions: comfortable with the terminal and shell.
- Scripting: Python or Bash for simple automation and parsing logs.
Spend time hands on: set up a small home lab, use virtual machines, and practice commands daily to build muscle memory.
How should you structure a step by step learning roadmap?
Start with fundamentals, then move to hands on labs, certifications, and real projects in that order. A staged approach reduces overwhelm and aligns learning with what employers expect from freshers.
- Month 1–2: Networking, Linux, and one scripting language.
- Month 3–4: Intro to security concepts, basic vulnerability types, and using beginner tools.
- Month 5–8: Focused labs on penetration testing, web security, and system hardening.
- Month 9–12: Certifications, a portfolio of projects, and internship or bug bounty participation.
Use small milestones and publicly visible work to document progress, such as writeups, GitHub repos, and Capture The Flag results.
Which tools should beginners learn first?
Begin with widely used, beginner friendly tools that teach concepts more than complexity. Learning these tools will make practical exercises and labs meaningful.
- Nmap: network scanning and discovery.
- Wireshark: packet analysis and protocol inspection.
- Burp Suite Community: web proxy and simple web testing.
- Metasploit (basic use): exploit validation in controlled labs.
- OWASP ZAP: web vulnerability scanning for beginners.
Pair each tool with a short project: scan your own VM, intercept traffic on a test app, or find deliberately placed vulnerabilities in training labs.
Which certifications are worth pursuing for freshers?
Choose certifications that validate practical skills and are recognized by hiring managers in India. They should complement hands on experience and show you can work in a professional context.
Consider certifications and program options such as cybersecurity certification programs that combine labs and placements. These programs often teach applied skills and provide interview support.
| Certification | Why it helps | Best for |
|---|---|---|
| CompTIA Security+ | Good for basics of security, vendor neutral. | Beginners wanting structured theory plus practical tasks. |
| CEH (CEH v13) | Recognized for ethical hacking concepts and tools. | Entry level penetration testing awareness and fundamentals. |
| Practical pentesting course with labs | Shows hands on competence and lab experience. | Freshers aiming for pen testing or SOC roles. |
When mentioning CEH, you can also investigate specific offerings such as the CEH v13 AI-powered course that blend modern labs with certification preparation.
Where should you train and practice safely?
Train in a legal, controlled environment using labs, virtual machines, and purpose built platforms. Never practice on systems you do not own or on production networks.
- Use platforms like TryHackMe and Hack The Box for beginner friendly labs.
- Build local VMs with intentionally vulnerable images for guided practice.
- Document every exercise and create short writeups for your portfolio.
If you are looking for structured instructor led programs, consider reputable options such as certified ethical hacking training that include labs and placement guidance.
How do you build a hiring-ready portfolio?
A hiring-ready portfolio includes project writeups, a GitHub repo, lab certificates, and a short CV listing practical tasks you completed. Recruiters want to see evidence you can apply your skills.
- Write five short reports: scanning, basic exploitation, web vuln, privilege escalation, and remediation suggestions.
- Publish code snippets and small scripts to GitHub with README explaining purpose.
- List completed training labs and any badges from platforms you used.
Keep the portfolio concise and focused: 4–6 strong items that show depth, not dozens of shallow tasks.
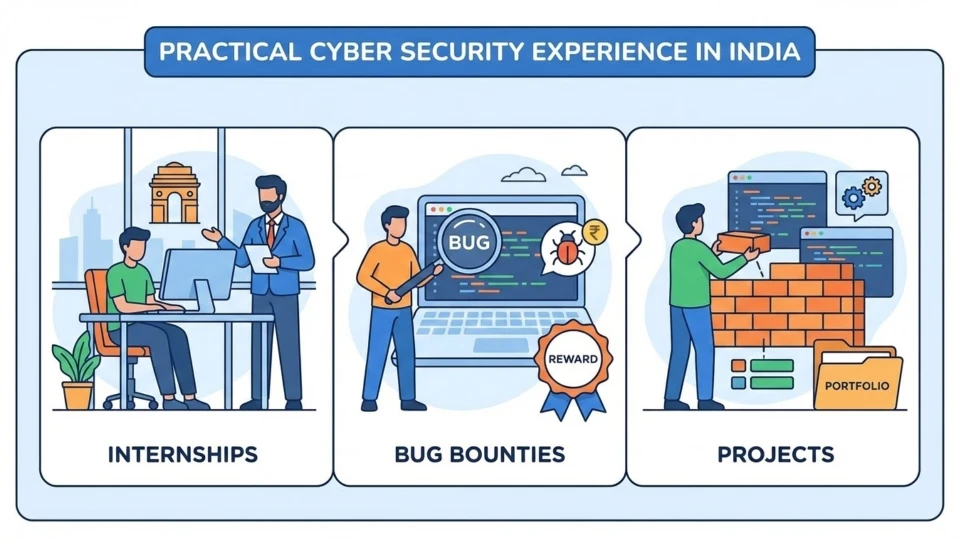
How to get practical experience: internships, bug bounties, and projects?
You can get practical experience through internships, volunteer projects, and responsible bug bounty participation. Each path builds credibility and demonstrates work readiness.
- Internships and helpdesk roles: start with junior security or IT support roles to get exposure.
- Bug bounties: begin with beginner friendly programs and follow disclosure rules; the bug bounty diploma program is an advanced learning route for structured practice.
- Open source contributions: help projects with security audits and simple fixes.
Record every valid finding and permissioned test in your portfolio and describe the mitigation steps you recommended.
What entry level roles can freshers expect and salary ranges?
Freshers can target roles such as security analyst, SOC analyst, junior penetration tester, and security operations engineer. These roles have clear entry points and training paths.
- SOC analyst: monitoring, alert triage, and incident logging.
- Junior penetration tester: guided client or lab engagements under senior supervision.
- Security analyst: vulnerability assessments, patch verification, and compliance checks.
Salary ranges vary by city and employer, but entry level security roles in India commonly start in the range of ₹3 to ₹6 lakh per year, rising quickly with certifications and demonstrable skills.
How to prepare for interviews and technical tests?
Prepare by practicing common tasks, explaining your methodology, and walking interviewers through a project from your portfolio. Communication is as important as technical skill in screening interviews.
- Practice live labs under time pressure to improve speed and clarity.
- Prepare short scripts explaining your thought process for scanning, exploitation, and remediation.
- Have 3 concise case studies ready from your portfolio to discuss in detail.
Mock interviews and peer review of your writeups can reveal gaps and improve clarity before real interviews.
What next after landing an entry level job?
After you land a role, focus on on the job learning, obtaining higher level certifications, and specializing in areas like cloud security, application security, or incident response. Career growth depends on continual practice and results.
- Seek mentorship and ask for hands on tasks beyond monitoring to learn faster.
- Plan a 12 month learning path for a specialization and follow it with projects.
- Contribute to team processes and write short internal reports to increase visibility.
Commit to measurable learning goals and track how your contributions improve team outcomes.
Can you build a cyber security career from scratch in India?
Yes, you can learn ethical hacking in India and build a cyber security career by following a structured roadmap, focusing on practical labs, and validating skills with projects and certifications. The market values demonstrable ability and consistent practice.
Start with the fundamentals, practice in legal labs, build a concise portfolio, target fresher friendly roles, and use certifications and internships to accelerate hiring. With steady work you can move from junior roles to specialist positions within a few years.